


Boar anatomy and physiology
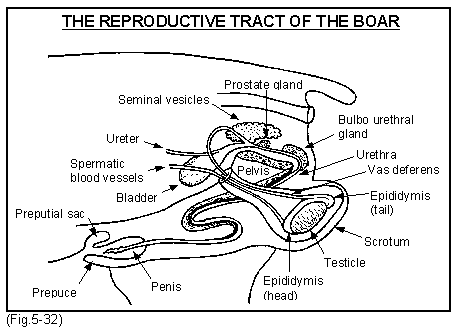
The male reproductive system (Fig.5-32) consists of two testicles, each of which is held almost vertically with the tail of the epididymis at the top. The epididymis is the area within which all the mature sperm is stored and held until ejaculation. From each testicle a tube, the urethra, carries the sperm into the abdomen via the inguinal canal. (If this hole is enlarged an inguinal rupture will be seen). From there it enters the neck of the bladder and continues in the groin down the penis to the exterior as the urethra. Thus from the neck of the bladder to the tip of the penis the urethra can carry either sperm or urine. There are three glands called the seminal vesicles, the prostrate and the bulbo urethral glands. The seminal vesicles produce the bulk of the ejaculate (300ml) and fructose to nourish the sperm. The prostrate gland provides other nutrients and the bulbo urethral gland the jelly that you often see at the end of mating
During service the sperm in the epididymis are pulsated down the urethra to be joined by the seminal fluids. This is a continuous process during the period of mating. You can see it if you stand behind the boar and you should check it when you supervise services.
The penis, which is long and rigid has a sigmoid or S - shape in its top half and an anti clockwise spiral at the end. It is 300-500mm long.
The preputial sack is filled with very smelly fluids including pheromones and it also has a very high bacterial content. The bacteria are potential pathogens and emptying the sac by squeezing at service increases the risk of infection entering the womb, particularly towards the end of the heat period.
Sperm is produced and matured under the influence of luteinising hormones (LH) and follicle stimulating hormones (FSH) and the whole process is controlled by the pituitary gland which is at the base of the brain.
Treatment for poor sperm quality is disappointing, however prostaglandins injected weekly are claimed to have some effect on libido. The evidence is not convincing.
The effects of age
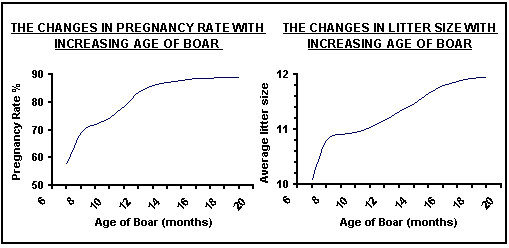
Boars reach puberty around 5 months of age but the amounts and quality of semen are usually insufficient at this age to fertilise efficiently. (Fig.5-33).
Frequency of mating
AGE: 7 - 8 months, mate twice weekly, 48 hours apart. 12 months onwards, mate 2 - 3 times weekly 24 hours apart.







