Scientific foundation explains efficacy of Excede® for Swine against SRD pathogens
A robust body of research explains the efficacy of Excede® for Swine (ceftiofur crystalline free acid) against four of the bacterial pathogens associated with swine respiratory disease (SRD).A third-generation cephalosporin, Excede for Swine is approved for treatment or control of SRD associated with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (APP), Streptococcus suis, Pasteurella multocida and Haemophilus parasuis.

To be clinically effective, explains Eva Jablonski, DVM, senior technical services veterinarian, Zoetis, the levels of Excede for Swine in plasma and tissues need to stay above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the target pathogens. MICs are the lowest concentration of a drug needed to prevent visible growth of a bacterium, and they are determined by pharmacokinetic analyses.
Plasma levels
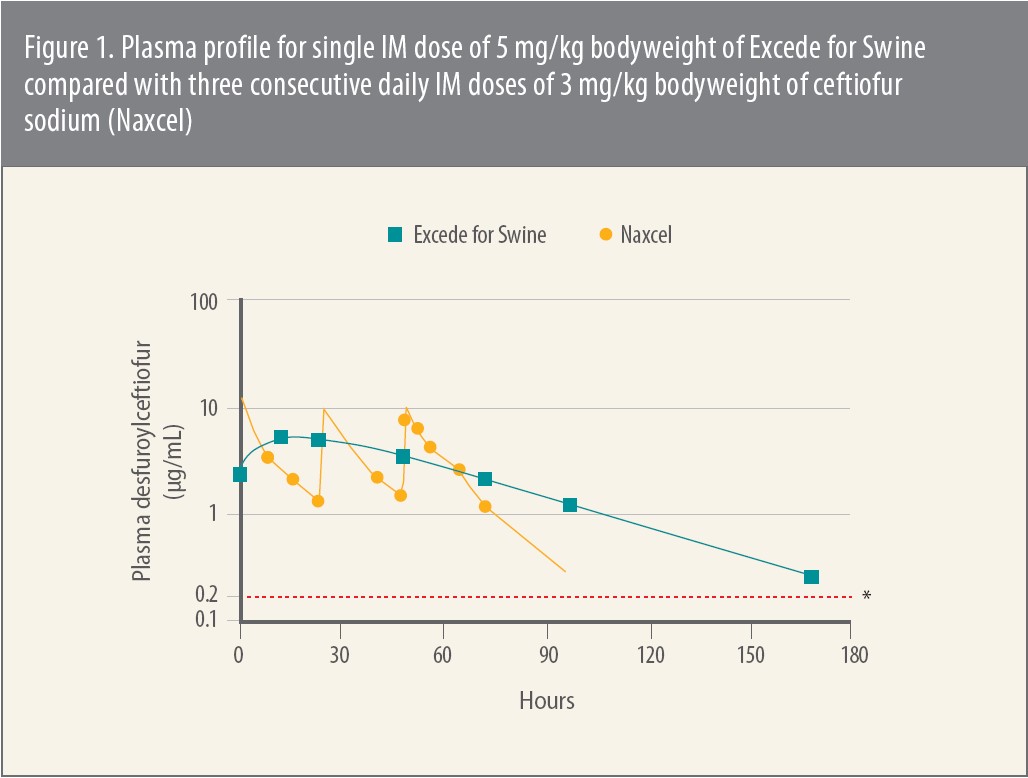
In one of the initial pharmacokinetic analyses Jablonski cites, investigators administered a single intramuscular (IM) dose of Excede for Swine to pigs as recommended on the label.1 Next they assayed plasma samples for ceftiofur and for metabolites related to desfuroylceftiofur (DFC), which Jablonski says is the major active metabolite of ceftiofur. These assays were performed before administration of Excede for Swine and from 1 to 240 hours afterward.
Therapeutic plasma levels of ceftiofur and the DFC-related metabolites were reached within 1 hour of administration — 2.23 ± 1.08 ug/ml — which was the earliest time point evaluated (Figure 1). The levels remained above established MICs for more than 7 days for the target pathogens APP, P. multocida, H. parasuis and S. suis. 2 That’s substantially longer than for a full, 3-day dosing regimen for ceftiofur sodium (Naxcel®) at 3 mg/kg bodyweight, the investigators noted. “These MIC values are still relevant,” Jablonski notes.3
Tissue concentration
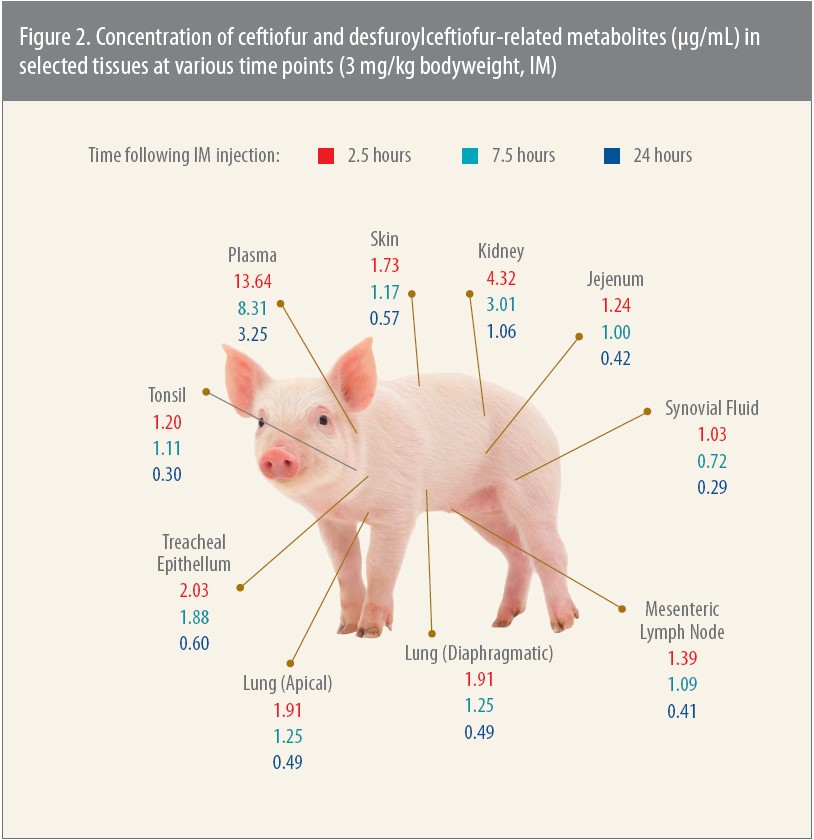
An earlier, pivotal pharmacokinetic study focused on tissue levels in pigs after an IM injection of Excenel® (ceftiofur hydrochloride).4 The study is relevant, Jablonski says, because Excenel, now sold as Excenel RTU EZ, has the same principal active metabolite — DFC — as Excede for Swine.
When investigators tested tissue levels for up to 24 hours after injection, the concentration of DFC was once again greater than the MICs for the pathogens tested, which in this study were APP, P. multocida and S. suis (Figure 2).
“Veterinarians often want to know about the tissue levels of an antibiotic,” Jablonski says. “H. parasuis, for example, is a cause of respiratory disease but can also lead to other problems like arthritis. S. suis, which is often secondary to viral infections such as porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome disease, is a cause of pneumonia, but it can also cause arthritis as well as polyserositis and a host of other clinical conditions.”
Absorption rates
The levels of Excenel or Naxcel peak and diminish from the site of injection within 24 hours. In contrast, absorption from the injection site with Excede for Swine is sustained — for at least 7 days — because of the antimicrobial’s unique, extended-release properties, Jablonski says.
Which of the three ceftiofur products to choose depends on the pathogens involved. The indications for the three antimicrobials differ somewhat, but there is also overlap. All three, for example, are indicated for APP. A producer therefore might choose one over the other based on the required withdrawal time, which is 4 or 6 days for Excenel RTU EZ depending on the regimen used, 4 days for Naxcel and 14 days for Excede for Swine.
Antimicrobial-susceptibility surveillance
Since antibiotic resistance is a concern to both veterinary and human medicine, surveilling the susceptibility of pathogens to various antimicrobials is of paramount importance, Jablonski continues. As part of an antibiotic-surveillance program that was initiated in 1997, Zoetis continues to collect hundreds of swine bacterial isolates from laboratories in the US and Canada and test them for pathogen sensitivity.
“The most recent data from 2019 demonstrate that MIC values for ceftiofur against the SRD pathogens — APP, P. multocida and S. suis — remain very low. The results are consistent with those from the previous 2 decades, which tells us that these ceftiofur-targeted SRD pathogens are still extremely sensitive to this antimicrobial,”5,6 Jablonski says.
Canadian researchers have had similar results, according to a study published in 2019.7 For ceftiofur, enrofloxacin, florfenicol, tilmicosin and tulathromycin, they determined MIC values as well as the “mutant prevention concentration” against APP, P. multocida and S. suis.
Mutant bacterial cells are believed to arise spontaneously when there is a high density of bacteria — bacterial densities of 107 to 109 or greater colony forming units/ml. “Antibiotic drug concentration inhibiting the growth of the least susceptible [cells] in these high-density populations has been termed the mutant prevention concentration (MPC),” the investigators say.
Ceftiofur and enrofloxacin had lower MIC and MPC values than did the other drugs.8 “Dosing to achieve or exceed the MPC…prevents growth of bacterial cells with reduced susceptibility,” say the investigators, and add that “optimization of therapy while minimizing the potential for antimicrobial resistance are major principles for antimicrobial stewardship.”
Comparative APP challenge
The efficacy of Excede for Swine suggested by in vitro pharmacokinetic analyses has been substantiated in a challenge study and field trial. As an example, Jablonski cites a comparative study with pigs that were treated with either Excede for Swine or enrofloxacin either 3, 5 or 7 days before investigators administered a challenge with APP.9
Pigs that received Excede for Swine had significantly (P ≤ 0.05) lower mortality and total lung lesion scores compared to the enrofloxacin groups, which she says can likely be attributed to Excede for Swine’s extended duration of activity. They also had significantly less growth of S. suis compared to those treated with enrofloxacin.
Multiple-site field efficacy study
The field trial with Excede for Swine involved more than 700 pigs and was conducted at multiple sites in several states.10 Excede for Swine or saline was administered to mixed-sex commercial pigs. Multiple SRD pathogens were isolated from the lung tissues of pigs in the study: APP, H. parasuis, P. multocida and S. suis.
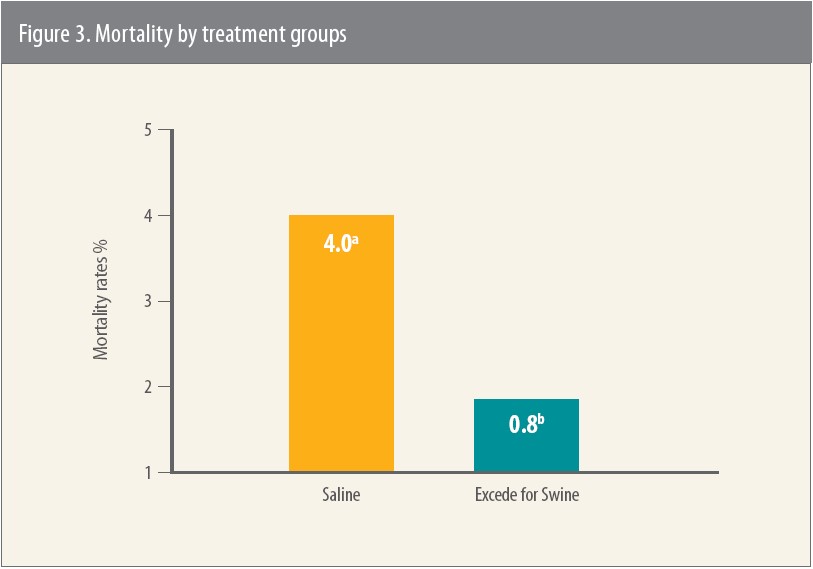
Pigs treated with Excede for Swine had significantly less mortality and fewer lung lesions compared to the saline control group, and there were no adverse events attributed to treatment with Excede for Swine (Figure 3).11
“Pharmacokinetic analyses, challenge studies and field trials as well as antimicrobial-sensitivity surveillance provide a solid scientific foundation for Excede for Swine,” Jablonski says. “Used wisely and judiciously, this valuable antimicrobial should continue to provide an effective treatment for SRD well into the future.”
Important safety information
People with known hypersensitivity to penicillin or cephalosporins should avoid exposure to EXCEDE FOR SWINE. Do not use in swine found to be hypersensitive to the product. Pre-slaughter withdrawal time is 14 days following the last dose. Click here to see full Prescribing Information.
All trademarks are the property of Zoetis Services LLC or a related company or a licensor unless otherwise noted.
| References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hibbard B, et al. | ||||
| (2004) | Pharmacokinetics of Ceftiofur Crystalline Free Acid in Swine.. Proceedings of the 18th IPVS Congress, Hamburg, Germany | Volume 2. | ||
| Ibid | ||||
| Sweeney M, et al. | ||||
| (2011 to 2015) | Antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus suis, and Bordetella bronchiseptica isolated from pigs in the United States and Canada. J Swine Health Prod. 2017 | 25(3):106-120 | ||
| Schionning S, et al. | ||||
| (August 1994) | Determination of tissue concentrations of desfuroylceftiofur in pigs after intramuscular injection of Excenel Sterile Powder.. 6th EAVPT Congress | |||
| Sweeney M, et al. | ||||
| (2011 to 2015) | Antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus suis, and Bordetella bronchiseptica isolated from pigs in the United States and Canada, | |||
| Leman AMR Roundtable Proceedings, | ||||
| (2019) | Mapping a course for responsible, effective antimicrobial use in swine. | pages 5-7 | ||
| Blondeau J, et al. | ||||
| (2019) | Mutant prevention and minimum inhibitory concentration drug values for enrofloxacin, ceftiofur, florfenicol, tilmicosin and tulathromycin tested against swine pathogens Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida and Streptococcus suis.. PLOS ONE | Volume 14(1) | ||
| Ibid | ||||
| Zoetis LLC | ||||
| Data on file, Study Report No. ORPORK 2030 | ||||
| Zoetis LLC | ||||
| Data on file, Study Report No. 1123C-60-08-315 | ||||
| Ibid | ||||