



Porcine Pleuropneumonia: Importance of a Broad Vaccine Induced Protection
Porcine pleuropneumonia due to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (Ap) is a highly contagious disease which still remains causing significant losses to the swine industry, writes Roman Krjci, Swine Corporate Technical Manager, Ceva Animal, France.The majority of contaminated farms deal with the chronic forms in which pigs having persistent lung and pleurisy lesions do not match their growth potential. Outbreaks with the increased mortality of cutely infected pigs occur mainly when the immunity is compromised or a new serotype appears in the herd.
Country-Specific Serotypes
The serotype repartition is highly variable in different countries. Some serotypes may be more prevalent in a certain territory and are considered as ‘country-specific’, however usually, more serotypes occur in the same country (Table 1).
Table 1. The occurrence of major serotypes in different countries.
| Country | Major serotypes | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Denmark | 2,5,6 | Angen, 1998 |
| China | 7,1,2,3 | Qigai He, 2013 |
| Czech Republic | 2,9,12 | Satran, 2002 |
| Finland | 2 | Heinikainen, 2013 |
| Philippines | 3,5,11 | Torres, 2006 |
| Spain | 7,4,2 | Maldonado, 2009 |
| Taiwan | 1-9-11, 3 | Hsu, 2013 |
The presence and prevalence of various serotypes changes over time and serotypes not or less present in the past may become most important. For example in the UK serotype 3 was predominant in 2004, while in 2009 it was serotype 8.
Multiple serotypes are often identified within one herd and moreover different serotypes can be isolated from sows and fatteners on some farms. Even in the stable, low prevalence farms the risk of the outbreaks exists with occasionally exploding seropositivity, correlating with the increased incidence of pleurisy in slaughtered pigs (Figure 1).
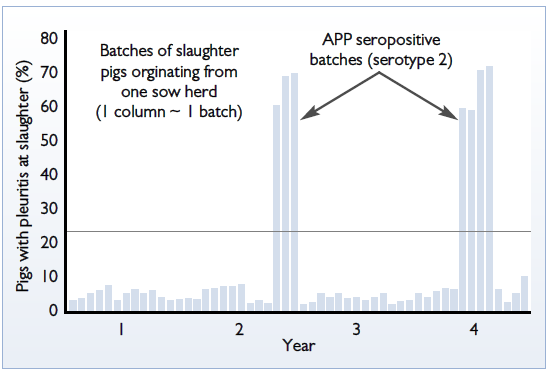
Exact Diagnosis Essential
In summary, the variability and presence of multiple serotypes maintain enormous demands on the exact diagnosis and also on the multi-serotype focused preventive measures. Besides the factors of virulence which are related to the lipopolysaccharide determinants of the serotype specificity, there are three Apx toxins which are significantly involved in the pathogenesis of pleuropneumonia.
Apx toxins are produced usually in couple in various combinations by differentserotypes. The active immunity against ApxI,ApxII and ApxIII then provides the protection independent on the serotype involved in the infection. That is why Coglapix, the vaccine against A. pleuropneumoniae developed by Ceva besides the LPS fraction, also expresses all Apx toxoids. Their presence was determined in the industrial antigens by immuneblotting.
Strong Immune Response
Coglapix elicits a strong immune response to Apx toxoids. Vaccinated rabbits seroconverted with significant titres of anti Apx antibodies two weeks after booster.The induced antibody titres were evaluated using three in-house Apx-specific competitive ELISAs based on specific monoclonal antibodies (Table 2).
Table 2. ELISA titres of Apx I, II and III specific antibodies in rabbits two weeks after the second vaccination with Coglapix.
| ApxI titre EU/ml) | ApxII titre (EU/ml) | ApxIII titre (EU/ml) |
|---|---|---|
| 50.9 | 19.2 | 10.0 |
The high degree of clinical protection induced by Coglapix, independent of the serotype specificity, has been demonstrated in numerous experiments.
The recent studies determined 24 weeks duration of protection against the challenge with Ap serotypes 1, 2 or 7.
Coglapix vaccinated pigs had significantly lower incidence and extension of the lung lesions in comparison to the non-vaccinated control (Tables 3 and 4).
Table 3. Incidence of lung lesions (%)
| Serotype 1 | Serotype 2 | Serotype 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coglapix | 35.3 | 38.1 | 17.6 |
| Control | 100 | 95.2 | 94.1 |
Table 4. Lung lesion scores
| Serotype 1 | Serotype 2 | Serotype 7 | |
| Coglapix | 11 | 15 | 5 |
| Control | 100 | 149 | 114 |
Such long-lasting immunity provides efficient prevention even in farms raising heavy pigs. The comparative trial with bacterin vaccines demonstrated superior efficacy of Coglapix in the protection against Ap serotype 5 (Figure 2).
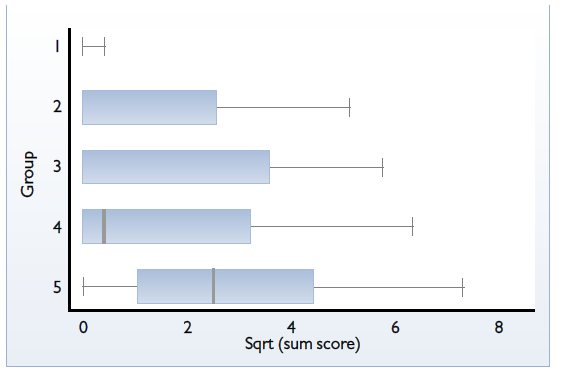
(1 = Coglapix, 2 = competitor toxoid vacine, 3 and 4 = bacterin vaccines, 5 = control).
The bacterin vaccines contained the homologous serotype antigens as the strain used in the challenge, while serotype 5 is heterologous for Coglapix. This fact confirmed the interest of vaccines providing cross serotype protection.
Conclusion
Multiple serotype presence in the pig farms and the continuous risk of the appearance of a new strain of different serotype in a particular farm requires a broad protection against all serotypes. Toxoid vaccines provide higher degree of active immunity than the bacterin ones in general, even against the serotypes which are homologous for the bacterin vaccines.
Coglapix conferred long lasting protection against Ap strains belonging to various serotypes and demonstrated its capability to prevent porcine pleuropneumonia in diverse conditions.
Further Reading
Find out more information on Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (Ap or App) by clicking here.
August 2014









