Pig outlook: Lean hog futures extend bull run
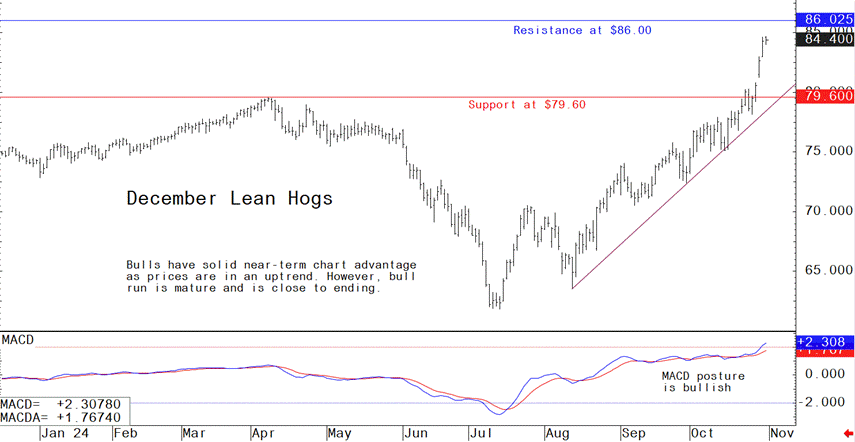
Livestock analyst Jim Wyckoff reports on global pig newsDecember lean hog futures prices this week soared to a contract high amid a steep price uptrend in place. Bulls are presently strong, but this week’s big gains suggest that a market top is now not far off. December lean hogs are technically overbought on the daily bar chart. The latest CME lean hog index is up another $1.05 to $86.78 as of Oct. 29, extending the string of gains to nine consecutive days, during which the index has jumped $2.92. Wholesale pork prices are also strong.
Latest USDA and other news regarding the global pork industry
1st case of H5N1 (avian influenza) case in Oregon in swine
The first case of H5N1 bird flu in swine has been confirmed in an Oregon backyard farm. USDA's APHIS and Oregon state officials are investigating a backyard farm where H5N1 avian influenza was detected in poultry and, for the first time, in one of five pigs. Despite no signs of illness, the swine tested positive, and all were euthanized. Shared resources may have facilitated cross-species transmission. The farm has been quarantined, but USDA reassures there is no risk to the U.S. pork supply, and genomic sequencing shows no increased human transmissibility.
The National Pork Producers Council emphasized that there are no safety concerns about U.S. pork supply, noting the pork industry has worked with USDA’s APHIS since 2009 to monitor for swine flu.
“The entire pork industry remains committed to safeguarding food safety and human and animal health,” NPPC CEO Bryan Humphreys said in a statement.
The pigs on the Oregon farm were not intended for the commercial food supply, USDA said.
Of note: Pigs represent a particular concern for the spread of bird flu because they can become co-infected with bird and human viruses, which could swap genes to form a new, more dangerous virus that can more easily infect humans.
The case was one factor that drove the USDA to broaden its bird flu surveillance to include nationwide bulk milk testing, which the agency announced on Wednesday, USDA Secretary Tom Vilsack told Reuters in an interview.
"While it’s a different variation of the virus and it is tied to wild birds, it is a factor to make sure that we understand and appreciate exactly where the virus is in dairy" and in cattle, he said.
The detection is a warning for pig farmers to be on the lookout for further infections, said Marie Culhane, a professor of veterinary population medicine at the University of Minnesota who has researched flu viruses in swine.
"People need to start increasing their plans to deal with it if it should happen in another herd and another herd," Culhane said. "Pigs are just really good at picking up influenza viruses."
Weekly USDA US pork export sales
Pork: Net sales of 44,800 MT for 2024 were up noticeably from the previous week and up 16 percent from the prior 4-week average. Increases were primarily for Mexico (17,700 MT, including decreases of 200 MT), China (10,400 MT), Japan (4,800 MT, including decreases of 200 MT), South Korea (3,800 MT, including decreases of 500 MT), and Canada (2,900 MT, including decreases of 700 MT). Net sales of 200 MT for 2025 were primarily for New Zealand. Exports of 32,300 MT were up 1 percent from the previous week and 13 percent from the prior 4-week average. The destinations were primarily to Mexico (11,400 MT), Japan (4,100 MT), China (3,600 MT), South Korea (2,900 MT), and Colombia (2,700 MT).
USDA warns of illegally imported meat in multi-state health alert
USDA's Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) issued a health alert concerning meat and poultry products illegally imported and sold in several U.S. states without official inspection marks. The affected products, found in Arizona, California, Iowa, Kansas, Maryland, Minnesota, Nebraska, Oklahoma, and Texas, include items such as "BEST Beef Curry" and "Eain Chak Coconut Soup Paste." While no illnesses have been reported, consumers are urged to discard or return the products. The investigation is ongoing as FSIS emphasizes the public risk posed by uninspected imports.
Of note: FSIS does not refer to the products as coming from Burma. However, they do note that you can view the labels in Burmese.
USDA releases report on US feedlot practices, highlights health and antibiotic use.
USDA’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) has published the first findings from the 2021 study of US feedlots, conducted by the National Animal Health Monitoring System (NAHMS). The report, based on data from 22 states, provides insights into cattle management practices, antibiotic use, and veterinary services across the feedlot industry.
Highlights from the report include:
- • Cattle origins: 54.7% of cattle placed in feedlots came directly from known operations, such as cow-calf or stocker facilities, while 38.2% were purchased from sale barns with unknown health histories.
- Identification practices: 85.4% of feedlots used ear tags for individual cattle identification, with 65.5% of cattle identified either before or upon arrival at the feedlot.
- Antibiotic and hormone claims: Most cattle (85.1%) were placed without meeting specific antibiotic or hormone-free marketing claims. Only 8.4% of cattle met limited or no-antibiotic claims, and 10.2% met no-hormone claims.
- Antibiotic use by feedlot size: Smaller feedlots (65.4%) were less likely to use antibiotics in feed compared to medium, large, and very large operations, which reported usage rates around 35-37%.
- Veterinary services: In 2020, 85.1% of feedlots used veterinarians. Larger operations were more likely to seek veterinary care, with 99.2% of very large feedlots using a veterinarian, compared to 81.2% of small feedlots.
The study also found that 64.2% of feedlots felt adequately prepared to manage the 2017 Veterinary Feed Directive (VFD) rule changes, citing access to resources and veterinary expertise. This report offers an important glimpse into the evolving practices of the U.S. feedlot industry.
FDA approves continued use of animal feed ingredients after MOU with AAFCO expires
FDA issued final guidance allowing the continued use of animal feed ingredients that were previously approved under a now-defunct Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). This MOU, in place since 2007, facilitated the collaboration between the FDA and AAFCO in reviewing and defining animal feed ingredients. However, the MOU expired on Oct. 1 and will not be renewed.
Key points of the new guidance:
- Continuation of ingredient use: The FDA has stated that it does not plan to initiate enforcement actions against the use of ingredients that were defined and listed in the 2024 AAFCO Official Publication (OP), even if they are not approved as food additives or generally recognized as safe (GRAS). This means that manufacturers can continue using these ingredients as long as they adhere to the intended use, specifications, and limitations outlined in the AAFCO OP.
- New consultation process: With the expiration of the MOU, the FDA has introduced a new Animal Food Ingredient Consultation (AFIC) process. This interim process allows firms to engage with the FDA regarding new ingredient reviews that would have previously gone through AAFCO. The AFIC aims to provide a pathway for firms to consult with the FDA about new ingredients and involves public input on safety concerns.
- Public and industry input: The FDA is actively seeking comments from industry stakeholders on its pre-market animal food review processes, including the Food Additive Petition (FAP) and GRAS programs. These comments will help determine if changes are needed to improve these pathways.
Of note: Despite the end of the MOU, the FDA plans to continue working with AAFCO and state regulators to ensure animal food safety. The agency will still participate in AAFCO committees and meetings.
Investigation reportedly uncovers animal cruelty at PQA Plus-certified farms
A recent investigation by Mercy For Animals has revealed instances of animal cruelty at farms certified under the Pork Quality Assurance Plus (PQA Plus) program. The investigation documented severe mistreatment of pigs, including animals suffering from prolapses being kicked, piglets castrated without pain relief, and sows confined in gestation crates. These practices starkly contradict the humane standards that the PQA Plus program is supposed to uphold.
Mercy For Animals released a white paper (link) detailing additional alleged violations, raising concerns about the effectiveness of the PQA Plus certification in ensuring humane treatment of pigs. Paula Tejeda-Moncrief, director of investigations for Mercy For Animals in the U.S., criticized the program, stating that marketing labels often fail to reflect the reality of animal treatment on farms.
In response to the allegations, Jason Menke, a spokesperson for the National Pork Board, stated that they are reviewing the white paper. He emphasized that about 85% of U.S. pigs are raised on PQA Plus site-assessed farms and reassured consumers about the welfare standards in place. Menke also mentioned that the PQA Plus program is continuously updated, with a new version set to be released next year.
The PQA Plus program was established to improve food safety and animal welfare in pork production. It involves training and certification for farmers and on-farm assessments conducted by certified advisors.
The next week’s likely high-low price trading ranges:
- December lean hog futures--$80.00 to 87.50 and with a sideways-lower bias
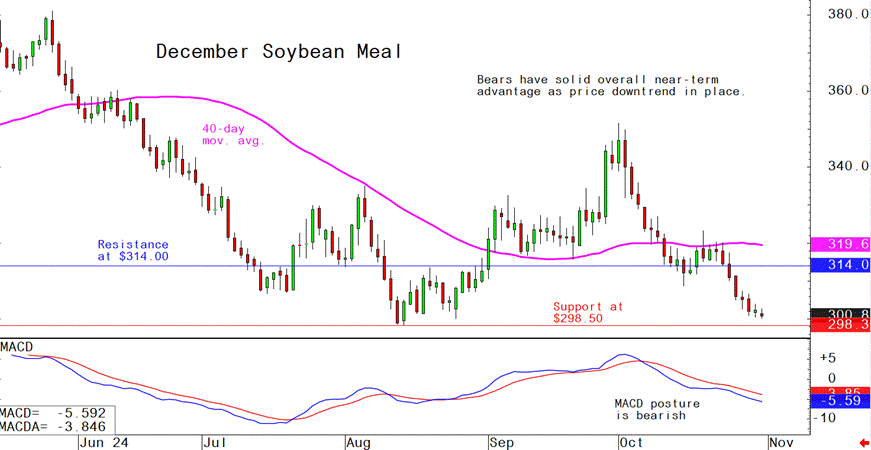
- December soybean meal futures--$298.50 to $315.00, and with a sideways bias
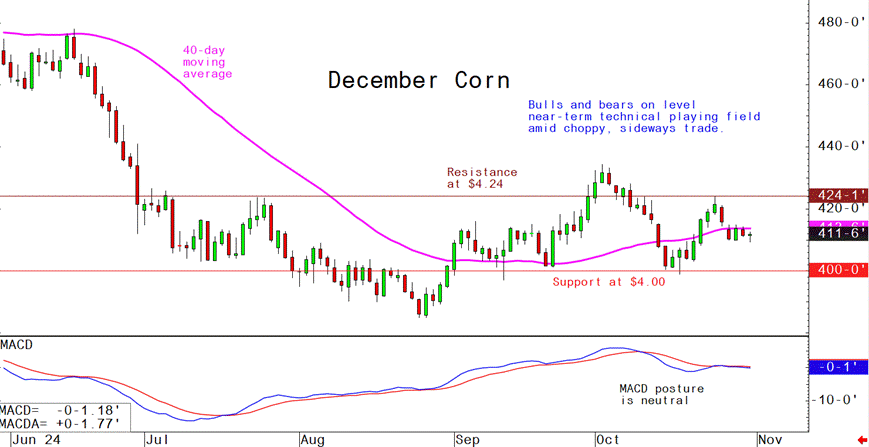
- December corn futures--$4.00 to $4.24 and a sideways bias
Latest analytical daily charts lean hog, soybean meal and corn futures