Field trial proves vaccine against edema disease is safe and efficacious
A multicenter, randomised field trial tested the efficacy and safety of VEPURED®, a new vaccine against Edema disease in pigs.Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate under field conditions the efficacy and safety of VEPURED®, a new recombinant vaccine against edema disease in pigs. The study was conducted on five commercial farrow-to-finish pig farms, which had historical records of clinical signs and presented F18-positive E.coli producing Vt2e. The study was designed as a multicenter, randomised, placebo-controlled, blinded field trial comparing VEPURED®vaccine to a placebo (phosphate-buffered saline).
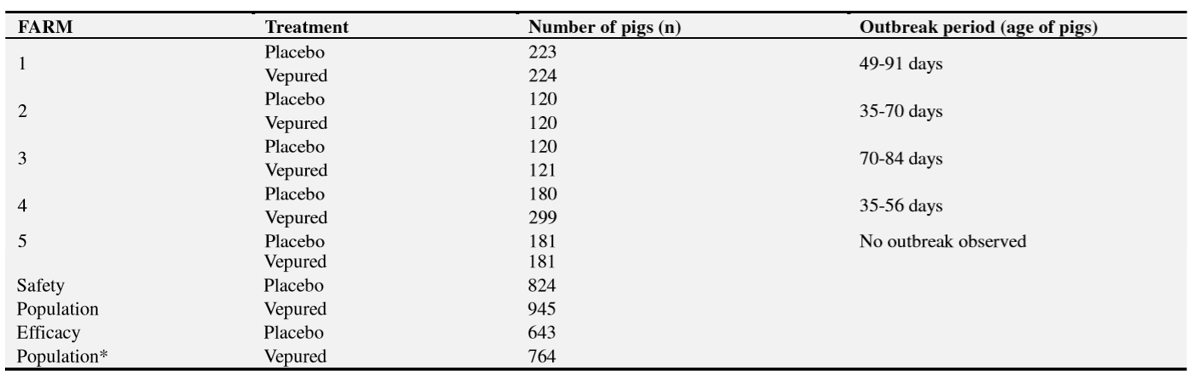
Animals, at the age of 2-3 days, were administered intramuscularly with 1 ml of VEPURED®(n=945) or with 1 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (n=824). After product administration, animals were followed-up until slaughter. During this period, several efficacy and safety parameters were evaluated.
On each farm, animals from both groups were held in the same unit and subjected to the same husbandry practices throughout the study. Clinical outbreaks of edema disease were only reported on four farms.
On these farms, vaccination with VEPURED®resulted in a statistically significant reduction in both the mortality rate and the occurrence of clinical signs related to the disease. A statistically significantly higher mean growth performance was also reported in the vaccinated group compared to the placebo group. In the farm without clinical outbreak of edema disease, differences were also observed in growth performance in favour of the vaccinated group.
No systemic reactions were observed during or immediately after vaccination with VEPURED®. Only mild transient local reactions, and slight clinically non-relevant temperature increases were reported in some animals. The results obtained in this study demonstrate that vaccination with VEPURED®is safe and efficacious against naturally occurring edema disease infection.
1. Introduction
Edema disease (ED) is an enterotoxemia caused by certain Escherichia coli (E.coli) colonising the small intestine and producing verotoxin 2e (Vt2e, also known as Stx2e) [1]. This toxin is absorbed from the intestine into the bloodstream where it damages the endothelial cells in target tissues [2, 3]. The endothelial cell damage induces an increase in vascular endothelium permeability resulting in edema. ED is mainly observed in recently weaned piglets, although it can also be observed during the growing and finishing phases [1].
The clinical manifestations of ED include palpebral edema, neurological signs such as ataxia, convulsions, paralysis and rigidity, and death [4, 5, 6]. The gross lesions of ED include subcutaneous edema, most often in the eyelids and face, and edema in the submucosa of the stomach, particularly in the glandular cardiac region. Moreover, the mesocolon of affected is commonly edematous. In addition, these animals usually have a decrease in weight gain, causing financial losses on commercial farms [6, 7].
Control of ED can be based on antimicrobial therapy. However, the efficacy of antibiotics usually comes too late because Vt2e has already been absorbed into the circulation when clinical signs become apparent [1, 2]. Furthermore, with on-going international pressure to decrease antibiotic use in agriculture owing to its perceived link to increasing antibiotic resistance [8, 9, 10, 11], development of efficacious vaccines is required to induce a protective immune response against this disease.
Extensive research is ongoing to develop safe and effective vaccines to prevent ED [12, 13, 14]. As a consequence of this extensive research, different vaccines have been registered in the last years. Edema vac (ARKO Labs) is composed of an avirulent live E.coli, for vaccination of 18-day-old piglets, that has demonstrated reduction of mortality associated with ED. Ecoporc Shiga (IDT) is composed of recombinant Stx2e with aluminium hydroxide as adjuvant. It is administered to 4-day old piglets, and confers a protection from 21 to 105 days after vaccination, reducing clinical signs and mortality associated with edema disease [15]. VEPURED®(Laboratorios HIPRA) is a new single-dose vaccine composed of a purified recombinant Vt2e with aluminium hydroxide and DEAE as adjuvants [16]. In pre-clinical trials performed under experimental conditions, this formulation was confirmed to be safe when administered to 2-day-old-piglets, conferring them effective protection against Vt2e-induced toxemia, reducing clinical signs and preventing mortality from 21 days to at least 112 days after vaccination [17]. However, clinical trials were needed to confirm the efficacy of VEPURED®against ED under natural infection.
The present clinical trial was performed in order to confirm the efficacy and safety of VEPURED®against ED when administered under field conditions.
2. Materials and methods
The study was approved by the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety (ANSM) (License no. EC-00761-0) as well as by the Belgian Federal Agency for Medicines and Health Products (FAMHP) (License no. 0002387). A written informed consent was signed by the participating farm owners prior to the enrolment of their animals in the study. The study was conducted in compliance with the Good Clinical Practice Guidance Document #85, May 9, 2001 (VICH GL9) [18].
2.1. Test product
VEPURED®vaccine (Laboratorios HIPRA). 1 ml of VEPURED® vaccine contains 600 UEMA (ELISA Units of Antigenic Mass) of recombinant Vt2e adjuvanted with 2,117 mg of aluminium hydroxide and 10 mg of DEAE.
2.2. Farms and animals
The study was carried out by three teams of swine practitioners on five commercial pig farms; three in France and two in Belgium. The five farms were selected after confirming they fulfilled the following selection criteria: to have had historical records of clinical signs and mortality due to ED, and to have been confirmed the presence of F18 positive E.coli producing Vt2e on faecal samples of animals from a previous batch.
The five farms were farrow-to-finish with a farrowing rhythm of 3-weeks. Animals were weaned at 21 days in all farms. Space, feeding and water requirements were met according to the regulatory requirements. Standard diets corresponding to each production phase were administered to the animals in all farms.
A total of 1,769 new-born piglets were included from July to August 2015 after confirming they fulfilled the inclusion criteria: to be clinically healthy, to be 2–3 days old at vaccination and to have a body weight >1 kg.
2.3. Study design
The study was designed as a multicenter, randomised, placebo-controlled, double blinded field trial comparing VEPURED® vaccine to a placebo (phosphate-buffered saline).
One day before vaccination, piglets on each farm were eartagged and randomly allocated into two groups: VEPURED®group and placebo group, stratifying by sow and weight. The randomisation ratio was 1:1, except for one farm where an unequal ratio was implemented at the request of the owner of the animals as a condition for their inclusion in the study.
Piglets were administered the products at 2–3 days of age. Animals in the vaccinated group (n=945) were inoculated with 1 ml of VEPURED®and piglets in the placebo group (n=824) received the same amount of phosphate-buffered saline (Table 1). Both products were administered intramuscularly in the neck area.
To achieve blinding, one member of each team of practitioners oversaw product administration according to a blinding code provided by the sponsor while the other members were in charge of the follow-up of animals, being unaware of product identity until the end of the study.
After product administration, animals were followed-up until slaughter. During this period, several efficacy and safety parameters were evaluated. Intestinal swab samples from dead piglets and faeces samples from animals with clinical signs were collected for bacteriological confirmation of the clinical outbreaks of ED. In case of absence of animals with clinical signs, faecal samples where obtained before slaughter in order to check the possible presence of Verotoxigenic E.coli (VTEC). On each farm, animals from both groups were mixed in different pens and subjected to the same husbandry practices throughout the study.
2.4. Analysis populations
The efficacy population was defined as the set of all animals allocated in those farms presenting an outbreak of ED. The safety population was defined as the set of all animals being administered either the vaccine or the placebo, independently on the presence of an outbreak of ED in the corresponding farm.
2.5. Study outcomes
2.5.1. Efficacy
The primary outcomes of the study were ED mortality and occurrence of clinical signs of ED (dyspnea; palpebral or throat edema; tremors; extensor rigidity; paralysis; opisthotonos). Every day during the whole study, the farmer registered clinical signs of ED and the mortality. The diagnosis of mortality due to ED was based mainly on the clinical signs observations before death, and on the necropsy findings and bacteriological confirmation in case of sudden death. Necropsies of animals that died were performed by the corresponding veterinarian in each farm. The secondary outcome of the study was growth performance at the end of fattening. Animals were also weighed one day before product administration and on days 28, 42 and 115. In this sense weight at other periods was also analysed for descriptive reasons.
2.5.2. Safety
Occurrence of systemic reactions related to vaccination was monitored in all the animals included in the study. Rectal temperatures and local reactions at the injection site were recorded one day before vaccination, just before vaccination, 4 hours, 24 hours and 48 hours after vaccination in 120 animals per group randomly selected among the farms included. Assessment of local reaction at the injection site included presence or absence of inflammation and nodules. In case of presence of local reactions, the extension of the lesions was measured. Body weight increase between the day of vaccination and day 28 after vaccination was also evaluated. In addition, mortality by different causes other than those related to ED was compared between groups.
2.6. Analytical procedures and tools
2.6.1. Bacteriological diagnosis
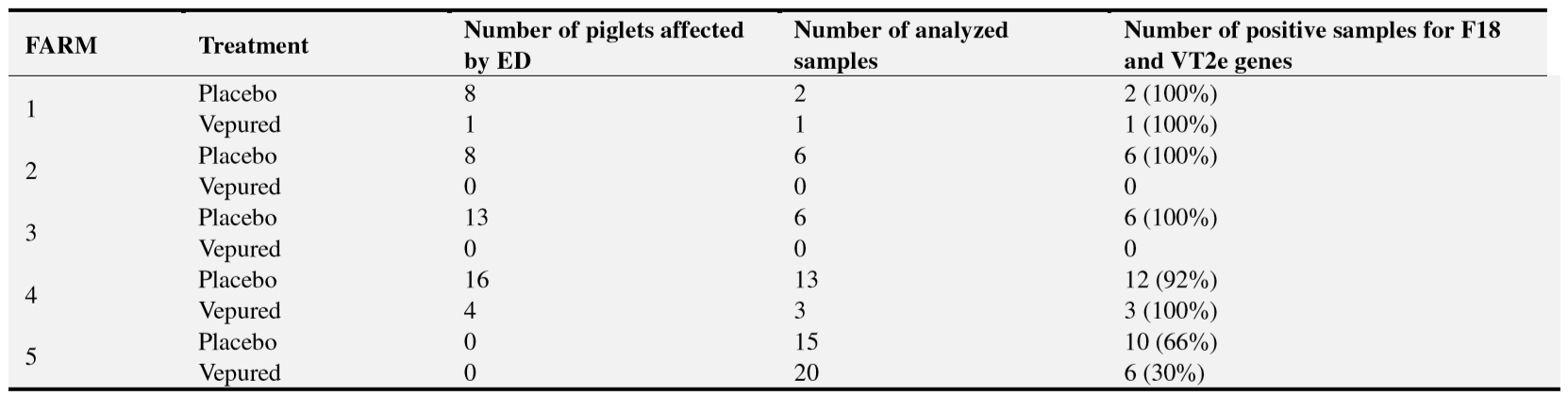
Rectal swabs from piglets with clinical signs or from healthy piglets at the end of fattening (in case of no clinical outbreak of ED) as well as intestinal content from piglets necropsied during the study were inoculated into 5 ml of peptone water and incubated at 37ºC overnight. Then, samples were cultured overnight at 37ºC on blood agar plates and on MacConkey agar plates. The blood agar plates were used to evaluate the presence of hemolytic E.coli in the samples. The cultured samples on MacConkey agar plates were used for confirming the presence of virulence factors related to Vt2e producing E.coli (adhesion F18 and toxin Vt2e) by PCR. The criteria used to identify VTEC as the causative agent were a nearly pure culture of hemolytic E.coli in blood agar plate and the presence of F18 and VT2e genes (virulence factor).
2.6.2. Detection of VTEC virulence factors by PCR
Bacterial samples from MacConkey agar plates were suspended on 1 ml of PBS. DNA from all bacteria-suspension samples was extracted using InstaGeneTM Matrix. Sterile PBS was used as a negative extraction control. All extracted samples, sterile water (PCR negative control) and known positive DNA from previous extraction (PCR positive control) were analysed by multiplex PCR. The primers used in the multiplex PCR (Table 2) and multiplex PCR protocol used were previously described [19].
Briefly, the QIAGEN Multiplex PCR Kit was used to amplify the genes for Vt2e and F18 by mixing PCR primers in a multiplex PCR reaction by following the manufacturer’s instructions. The multiplex PCR was completed by an initial heat activation of 15 min at 95ºC, then 25 cycles of 30 s at 94ºC, 90 s at 63ºC, and 90 s at 72ºC; and an extension of 10 min at 72ºC.
Multiplex PCR products were separated in a 1.5% agarose gel. References of positive control strain (VTEC 107/86) and 100 base-pair DNA ladder (New England BioLabs) were used to identify amplified products. Amplified PCR products were visualised with Gel Red 1.5X (Biotium) under an UV illuminator, and recorded using Doc-PrintVX5 (Vilber).
2.7. Statistical analysis
The experimental unit in the study was the piglet. The minimum sample size per group was estimated by a simulation of the expected results by the software Ene 3.0 [14-20]. Based on data from previous studies [15-21, 16-22], assuming a 6% mortality rate in the placebo group and an 80% lower rate in the vaccinated group (1%) on the farms affected by an outbreak of ED, the minimum total number of animals needed to detect, by means of a chi-square test for proportions, statistically significant differences between groups with a significance level of 5% and a power of 80% was 422 (211 pigs per group). Assuming a moderate incidence of outbreaks of ED among the participating farms and in order to achieve sufficient external validity, a total of five commercial farms (1,769 pigs) were finally included to achieve the minimum total sample size to evidence statistically significant differences, in the event some of the farms did not present an outbreak.
The software used for the statistical analysis was SAS Software v9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA). Quantitative variables were summarised using mean, standard deviation and sample size, while qualitative variables were summarised using relative and absolute frequencies. The significance level for all tests performed during the statistical analysis of data was set at alpha = 0.05. Binary response variables (Mortality by ED, Mortality by other causes and the presence of at least one clinical sign related to ED) were analysed by means of a generalised linear mixed model with binary response and logit link considering treatment group as a fixed effect and farm as a random effect. Lsmeans with the inverse logit transformation were used to estimate the corresponding incidences in both groups. Quantitative variables (Body weight at day 1, day 28, day 42, day 115 and at the end of fattening and Rectal Temperature at 4 hours) were analysed by means of a linear mixed model considering Farm as a random effect. Both variables referred to body weights were analysed after a log-transformation of values.
No interactions between farm and treatment were found in any of the models described. All models were validated using graphical analyses of the residuals.
Finally, in order to describe in detail the response variables, summaries were also presented at farm level.
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of efficacy
Clinical outbreaks of ED were reported on four out of the five farms after observing mortality and clinical signs related to the disease (Table 1). In the four farms, presence of F18-positive E.coli producing Vt2e was confirmed by bacteriological diagnosis in intestinal contents of dead piglets and faeces from animals with clinical signs (Table 3). On these farms all the study outcomes were evaluated.
Neither clinical signs of ED nor mortality were observed on the farm 5 although F18-positive E.coli producing Vt2e was detected in 46% (16/35) of the faeces samples collected from animals before slaughter. In this case, only the safety outcomes were evaluated.
3.1.1. Mortality
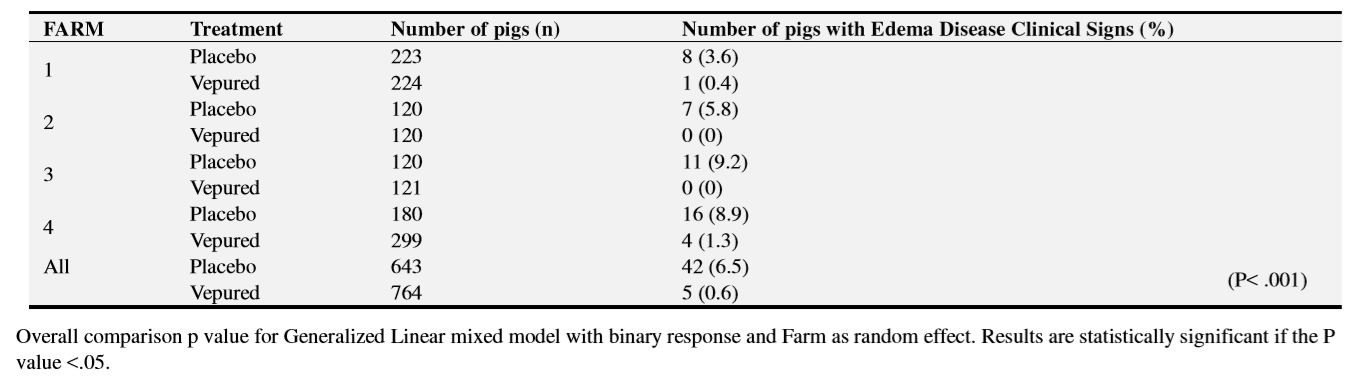
ED mortality was statistically significantly lower in the vaccinated group than in the placebo group (0.3% vs 4.0%; OR=16.06; P <.001) (Table 4). ED mortality in the placebo group was observed on all farms whereas ED mortality in the vaccinated group was only observed on two farms, where one death attributable to the disease was reported per farm.
Mortality attributed to other causes (evaluated considering the safety population) was not significantly different between groups, being 5.4% in the placebo group and 5.4% in the vaccinated group (OR=1.01; P=0.954).
3.1.2. Occurrence of clinical signs
Clinical signs of ED were observed in 6.5% of the pigs in the placebo group but in only 0.6% of pigs vaccinated (Table 5). The reduction in the incidence of clinical disease in the vaccinated group was statistically significant (OR=11.19; P <.001). Similar to mortality, clinical signs of ED in the vaccinated group were observed on only two farms.
Among animals with clinical signs of ED, 61.9% (26 out of 42) died in the placebo group and 40% (2 out of 5) died in the vaccinated group. The most prevalent clinical signs were Palpebral_Edema (34 animals in the placebo group vs 2 in the vaccinated group) and Paralysis (12 animals in the placebo group vs none in the vaccinated group)
3.1.3. Growth performance
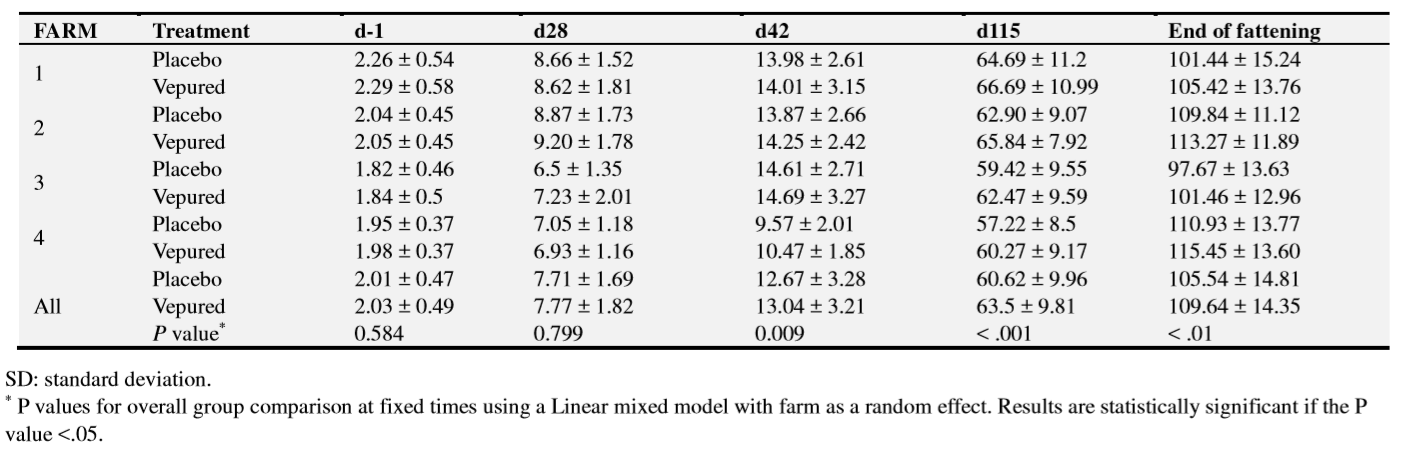
Differences between groups regarding animal weights were observed at day 42 (P=0.009), day 115 (P<0.001) and at the end of fattening (P<0.001). Data summarised for each farm show that differences in body weight between vaccinated and placebo groups were observed after ED outbreaks, as shown by weights at day 115 on the three farms where the outbreak occurred later and at day 42 on the farm where it occurred earlier (35-56 days) (Table 6).
On the farm where clinical ED was not observed, no differences in body weight were observed between the vaccinated and the placebo group before vaccination, on 28 and 42 days after vaccination. However, body weight was higher in the vaccinated group than in the placebo group on day 115 (58.49 kg vs 55.27kg) and at end of fattening (110.06kg vs 106.24 kg vs).
3.2. Assessment of safety
No systemic reactions related to the vaccination were observed during the study. Regarding to local reactions, only mild transient inflammation at the injection site (maximum 1.5 cm) was observed at the time point of higher incidence (four hours after vaccination) in both the vaccinated and the placebo groups. Specifically, 35% of the vaccinated animals and 14% of the placebo animals showed mild transient inflammation that spontaneously resolved without treatment.
Mean rectal temperature in the vaccinated group increased slightly four hours after vaccination and returned to baseline values after one day. When compared to the placebo group, no relevant differences in the mean temperature increase with respect to the baseline values were observed after vaccination. The maximum individual temperature increase in the first two days in the vaccinated group was 1.09ºC.
Finally, regarding body weight progression, no differences between the vaccinated and the placebo groups were observed on day 28 after vaccination, confirming absence of effect of the vaccine on this parameter.
4. Discussion
The efficacy of VEPURED®vaccine was previously tested in 2 day-old piglets after an experimental toxin challenge [17]. Although an experimental toxin challenge is a well described approach for evaluating efficacy of vaccines against ED [5, 14], clinical field studies are necessary to evaluate the efficacy of the vaccine against a natural infection, when F18-positive E. coli producing-Vt2e colonise the intestinal tract of the animals.
In this study vaccine efficacy against ED was evaluated on five commercial farms under field conditions. Clinical outbreaks of ED were reported in four out of five farms, from 14 to 49 days after weaning, which is the period when F18 positive E. coli producing-Vt2e strains most often cause ED [1]. During the ED outbreak, animals had palpebral edema, and neurological dysfunction and some died, which are the typical signs described for ED [1, 4, 5] and result from microangiopathy and vascular necrosis caused by Vt2e [1]. In farms with ED, the mortality rates were 0.3% and 4.0% for vaccinated and placebo groups respectively (OR=16.06; P < 0.001) and clinical signs related to ED were 0.6% vs. 6.5% for vaccinated and placebo groups respectively (OR=11.19; P <0.001). These results are in line with results obtained in the previous efficacy study, where vaccination with Ecoporc Shiga in a farm with problems of ED reduced overall mortality (1.3% vs 7.7%; OR=6.27) [22]. These results confirm that vaccines containing recombinant Vt2e are able to protect piglets form ED.
Also, these results are in line with those obtained in the previous efficacy study performed with VEPURED®, by using an experimental toxin challenge [17]. In that study mortality in the vaccinated was lower than in the placebo group (0% vs 92.3%), and the percentage of piglets showing clinical signs after challenge was also lower in the vaccinated group than in the placebo group both at 21 days after vaccination (57.14% vs 100% ) and at 112 days after vaccination (14.2 % vs 100%). The reductions of mortality and clinical signs were higher in the experimental study than in the clinical trial since experimental conditions guaranty the correct infection of all animals.
Vaccination with VEPURED®also improved body weight performance in farms with ED outbreak, at the end of fattening from 105.54 ± 14.81 kg to 109.64 ± 14.35 kg (P < 0.001), corresponding to 4.2 kg/pig in average for animals alive at the end of study.
Therefore, the results of the study confirm that vaccination with VEPURED®prevents the negative effects of natural infection with F18-positive E.coli producing-Vt2e on growth performance, as previously described by other authors [6, 21, 23, 24].
In previous studies, reduction in weight gain without clinical signs of ED in farms with F18-positive E.coli producing-Vt2e has been described as subclinical ED [1, 14, 25]. In this study, at day 115, animals from the placebo group from the farm without ED outbreak had statistically lower weight gain than vaccinated animals, and F18-positive E.coli producing-Vt2e was detected in faeces. These results suggest that this farm may have had a subclinical infection. However, no histopathological analysis looking for microvascular lesions described in subclinical cases of ED was performed in the present study to confirm it. In line with a previous report where an experimental vaccine was tested in a subclinical ED experimental model [14], in the present study it was demonstrated that intramuscular administration of an inactivated vaccine improved growth performance (3.82 kg/pig) even on the farm where no clinical signs or mortality related to ED were observed among the animals.
5. Conclusion
According to the results obtained in the present field study it can be concluded that VEPURED®is a really safe and effective new recombinant vaccine against naturally occurring ED infections. Vaccination of piglets with VEPURED®in farms endemic to F18-positive E.coli producing Vt2e with historical records of clinical signs of ED mainly results in a reduction in both the mortality rate and the occurrence of clinical signs, as well as in an improvement in growth performance at the end of fattening. In addition, the results of the study suggest that vaccination with VEPURED®also has a beneficial effect, in terms of growth performance improvement, in farms endemic to F18-positive E.coli producing Vt2e although without clinical signs of ED. Nevertheless, further research should be done in order to confirm this hypothesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Pascal Defoort, Ronan L'Helgoualch, Pascal Hourcq and George Graur, the independent practitioners who participated in the study, for their collaboration during the trials. We also thank Judit Moreno for her expert assistance in the immunological analysis, and Marc Guàrdia for his regulatory assessment. Finally, we thank Llorenç Badiella (SEA-UAB) for his assistance in the statistical analysis of the data.
| References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] Fairbrother J. M. and Gyles C. | ||||
| (2012) | Disease of swine, 10th. eds. Zimmerman J. J., Karriker L. A., Ramirez A., Schwartz K. J. and Stevenson G. W. Ames, Iowa. Chap 53 (Colibacilosis), 723-749. | |||
| [2] Casanova N. A., Redondo L. M., Dailoff G. C., Arenas D. and Fernández Miyakawa M. E. | ||||
| (2018) | Overview of the role of Shiga toxins in porcine edema disease pathogenesis. Toxicon. 15: 148154. | |||
| [3] Bergan J., Dyve Lingelem A. B., Simm R., Skotland T. and Sandwig K | ||||
| (2012) | Shiga toxins. Toxicon, 60(6): 1085-1107. | |||
| [4] Clugston R. E., Nielsen N. O. and Smith D. L. T. | ||||
| (1974) | Experimental edema disease of swine (E. coli enterotoxemia) III. Pathology and pathogenesis. Can J Comp Med, 38: 34-43. | |||
| [5] MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L. and Wilcock B. P. | ||||
| (1991) | Reproduction of oedema disease of swine with purified Shiga-like toxin-II variant. Vet Pathol, 28: 66–73. | |||
| [6] Bosworth B. T., Samuel J. E., Moon H. W., O'brien A. D., Gordon V. M. and Whipp S. C. | ||||
| (1996) | Vaccination with genetically modified Shiga-like toxin IIe prevents oedema disease in swine. Infect Immun, 64: 55-60. | |||
| [7] Bosworth B. T., Green R. A. and Morrison R. B. | ||||
| (1994) | Oedema disease: A search for a genetic link. J Swine Health Prod, 2(3): 1922. | |||
| [8] Teuber M. | ||||
| (2001) | Veterinary use and antibiotic resistence. Curr Opin Microbiol, 4: 493-499 | |||
| [9] Phillips I., Casewell M., Cox T., de Groot B., Friis C., Jones R., Nightingale C., Preston R. and Waddell J. | ||||
| (2004) | Does the use of antibiotics in food animals pose a risk to human health? A critical review of published data. J. Antimicrob Chemother, 53: 28-52. | |||
| [10] Kusumoto M., Hidoka Y., Fujii Y., Murata M., Miyoshi H., Ogura Y., Gotoh Y., Iwata T., Hayashi T. and Akiba M. | ||||
| (2016) | Emergence of a Multidrug-Resistant Shiga Toxin-Producing Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Lineage in Diseased Swine in Japan. J Clin Microbiol, 54(4): 1074-1081. | |||
| [11] Bednorz C., Oelgeschläger K., Kinnemann B., Hartmann S., Neumann K., Pieper R., et al. | ||||
| (2013) | The broader context of antibiotic resistance: zinc feed supplementation of piglets increases the proportion of multi-resistant Escherichia coli in vivo. Intl J Medical Microbiol. 303: 396–403. | |||
| [12] Won G., John Hwa L. | ||||
| (2017) | Potent immune responses induced by a Salmonella ghost delivery system that expresses the recombinant Stx2eB, FedF, and FedA proteins of the Escherichia coli-producing F18 and Shiga toxin in a murine model and evaluation of its protective effect as a porcine vaccine candidate. Vet Q. 37(1): 8190. | |||
| [13] Toshio S., Takeshi M., Eiji T., Yumiko K., Sou-Ichi M., Ko K., Kazutoshi S. and Takashi H. | ||||
| (2013) | Evaluation of Recombinant Forms of the Shiga Toxin Variant Stx2eB Subunit and Non-Toxic Mutant Stx2e as Vaccine Candidates against Porcine Edema Disease. J Vet Med Sci. 75(10): 1309–1315. | |||
| [14] Oanh T. K., Nguyen V. K., de Greve H. and Goddeeris B. M. | ||||
| (2012) | Oanh T. K., Nguyen V. K., de Greve H. and Goddeeris B. M. | |||
| [15] European Medicines Agency. | ||||
| (2013) | CVMP assessment report for ECOPORC SHIGA. Retrieved 04/12/2018 from | |||
| [16] European Medicines Agency. | ||||
| (2017) | CVMP assessment report for VEPURED. | |||
| [17] Mallorquí J., Simon-Grifé M., Ferrer-Soler L., Roca M., March R. and Sitjà M. | ||||
| (2018) | Reduced mortality and morbidity associated with verotoxin 2e-induced edema disease in pigs using a recombinant verotoxin 2e vaccine. J. Swine Health Prod. 26(5): 253-261. | |||
| [18] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Center for veterinary Medicine. | ||||
| (2001) | Guidance for industry: Good Clinical Practives. | |||
| [19] Zhang W., Zhao M., Ruesch L., Omot A. and Francis D. | ||||
| (2007) | Prevalence of virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains recently isolated from young pigs with diarrhoea in the US. Vet Microbiol, 123: 145-152. | |||
| [20] Badiella L. and Marino A. P. | ||||
| (2005) | Cálculo del tamaño muestral ™ con el programa Ene 2.0: manual del programa, documentación y ejemplos. eds. Gráficas Monterreina. Spain, Madrid. | |||
| [21] Johansen M., Andresen L. O., Jorsal S. E., Thomsen L. K., Waddell T. E. and Gyles C. L. | ||||
| (1997) | Prevention of oedema disease in pigs by vaccination with verotoxin 2e toxoid. Can J Vet Res, 61: 280285. | |||
| [22] Fricke R., Bastert O., Gotter V., Brons N., Kamp J. and Selbitz H. J. | ||||
| (2015) | Implementation of a vaccine against Shigatoxin 2e in a piglet producing farm with problems of Oedema disease: case study. Porcine Health Management, 1: 6. | |||
| [23] Gordon N. A., Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., O'Brien A. D. and Samuels J. E. | ||||
| (1992) | An enzymatic mutant of Shiga-like toxin-II variant is a vaccine candidate for oedema disease of swine. Infect Immun, 60: 485-490. | |||
| [24] Makino S. I., Watarai M., Tabuchi H., Shirahata T., Furuoka H., Kobayashi Y. and Takeda Y. | ||||
| (2001) | Genetically modified Shiga toxin 2e (Stx2e) producing Escherichia coli is a vaccine candidate for porcine oedema disease. Microb Pathog, 31: 1– 8. | |||
| [25] Gannon V. P., Gyles C. L. and Wilcock B. P. | ||||
| (1989) | Effects of Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxins (verotoxins) in pigs. Can J Vet Res, 53: 306-312. |